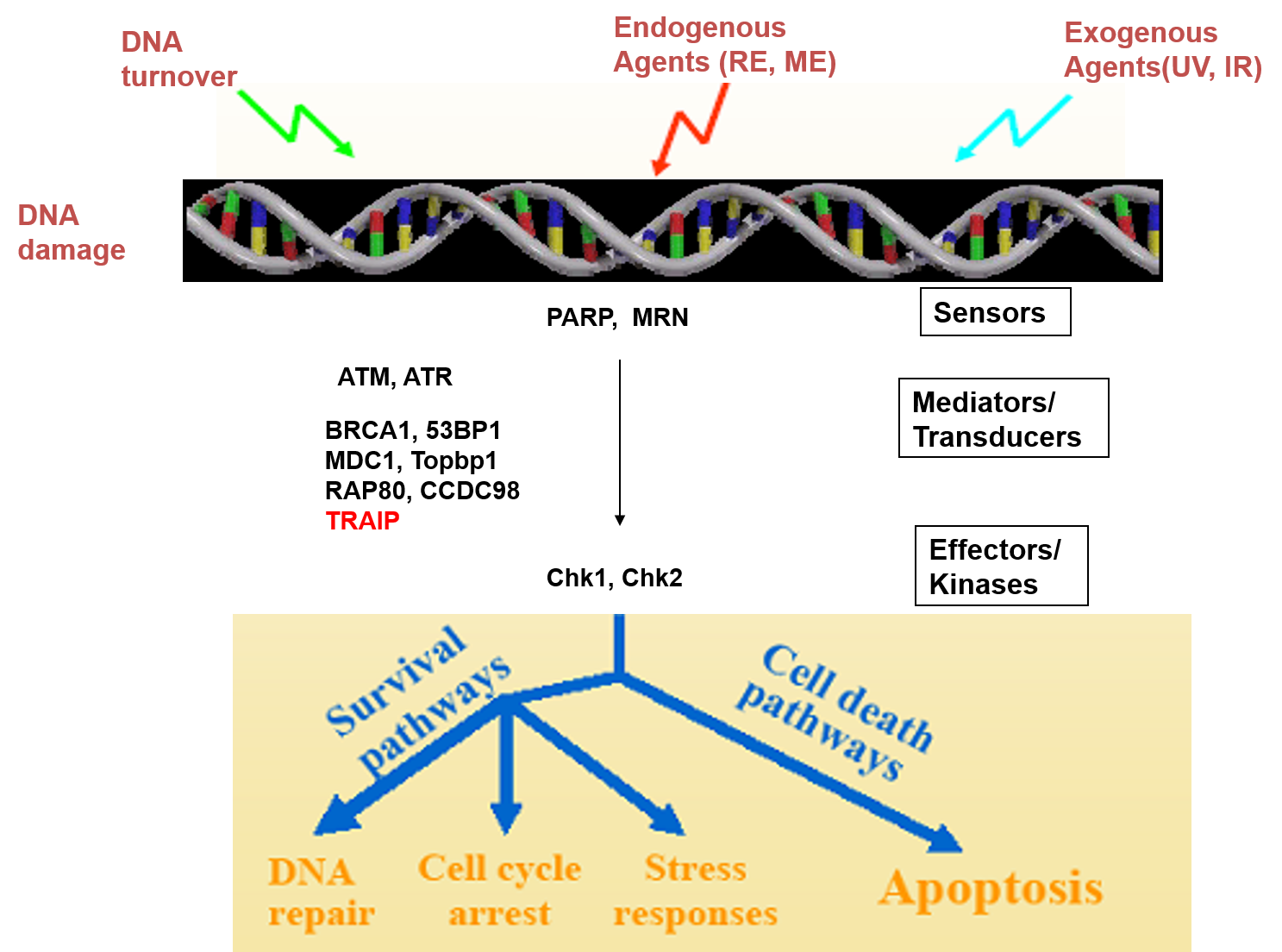
My lab focuses on studying the DNA damage response pathway and development/progression of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
DNA damage responses are important in maintaining genetic stability in eukaryotic cells. Because many tumor suppressor proteins including ATM, ATR, MDC1, RNF8, RNF168, RAP80, BRCA1, and BRCA2 are involved in the DNA damage pathway, the complete understanding of this pathway is important in preventing neoplastic transformation. So, our laboratory’s goal is to understand the inherent genetic stability and molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis by studying DNA damage signaling pathways. CML study is the second project in my Lab. My Lab has focused on identifying genes that are resistant to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor of CML. In addition, we are studying the molecular mechanisms of the discovered genes and applying them to CML patients. The aim of this research project is to ultimately contribute to the treatment and diagnosis of chronic myelogenous leukemia.
저희 연구실은 DNA 손상 반응 경로와 만성 골수성 백혈병 (CML)의 발병/진행을 중점적으로 연구하고 있습니다. DNA 손상 반응은 진핵세포에서 유전적 안정성을 유지하는 데 중요합니다. ATM, ATR, MDC1, RNF8, RNF168, RAP80, BRCA1 및 BRCA2를 포함한 많은 종양 억제 단백질이 DNA 손상 경로에 관여하기 때문에 이 경로에 대한 완전한 이해는 종양 발생을 예방하는 데 중요합니다. 따라서 우리 실험실의 목표는 DNA 손상 신호 경로를 연구하여 종양 발생의 유전적 안정성과 분자 메커니즘을 이해하는 것입니다. CML 연구는 저희 연구실의 두 번째 프로젝트입니다. 저희 연구실은 CML의 티로신 키나제 억제제에 내성이있는 유전자를 식별하는 데 중점을 두었습니다. 또한 발견된 유전자의 분자 메커니즘을 연구하여 CML 환자에게 적용하고 있습니다. 이 연구 프로젝트의 궁극적 목적은 만성 골수성 백혈병의 치료 및 진단에 기여하는 것입니다.
대표 논문
1. GCA links TRAF6-ULK1-dependent autophagy activation in resistant chronic myeloid leukemia.
Han SH, Korm S, Han YG, Choi SY, Kim SH, Chung HJ, Park K, Kim JY, Myung K, Lee JY, Kim H*, Kim DW*.Autophagy. 2019 Dec;15(12):2076-2090. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1596492. Epub 2019 Mar 30.PMID: 30929559 (*Corresponding Author)
2, Han SH, Kim SH, Kim HJ, Lee Y, Choi SY, Park G, Kim DH, Lee A, Kim J, Choi JM, Kim Y, Myung K, Kim H*, Kim DW*. (2017) Cobll1 is linked to drug resistance and blastic transformation in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia (*Corresponding Author)
3. Lee NS, Chung HJ, Kim HJ, Lee SY, JJi J, Seo Y, Han SH, Choi M, Yun M, Lee SG, Myung K, Kim Y, Kang HC, Kim H. (2016) TRAIP/RNF206 is required for recruitment of RAP80 to sites of DNA damage. Nature communication.
4. Baik SH, Fane M, Park JH, Cheng YL, Yang-Wei Fann D, Yun UJ, Choi Y, Park JS, Chai BH, Park JS, Back SH, Jeong JI, Jang YJ, Bahn G, Lee JY, Li YI, Sobey CG, Uchida T, Park JH, Kim HT, Tang SC, Arumugam TV, Jo DG. (2015) Pin1 promotes neuronal death in stroke by stabilizing Notch intracellular domain. Ann Neurol. 77(3):504-16
5. Lim S, Kim WJ, Kim YH, Lee S, Koo JH, Lee JA, Yoon H, Kim DH, Park HJ, Kim HM, Lee HG, Yun Kim J, Lee JU, Hun Shin J, Kyun Kim L, Doh J, Kim H, Lee SK, Bothwell AL, Suh M, Choi JM. (2015) dNP2 is a blood-brain barrier-permeable peptide enabling ctCTLA-4 protein delivery to ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat Commun.15;6:8244
6. Huang J, Huen MS, Kim H, Leung CC, Glover JN, Yu X, Chen J. (2009) RAD18 transmits DNA damage signalling to elicit homologous recombination repair. Nat Cell Biol. 11(5):592-603.
7. Kim H, Lee JE, Shin ES, Yoo YK, Cho JH, Yun MH, Kim YH, Kim SK, Kim HJ, Jang TW, Kwak SM, Kim CS, Ryu JS. (2008) Effect of BRCA1 haplotype on survival of non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 26(36):5972-9.
8. Hongtae Kim, Jun Huang & Junjie Chen (2007) CCDC98 is a BRCA1-BRCT domain?binding protein involved in the DNA damage response. Nature structure& Molecular biology. 14 : 710-715
9. Hongtae Kim, Junjie Chen* and Xiaochun Yu* (*To whom correspondence should be addressed) (2007) Ubiquitin-binding protein mediates BRCA1-dependent DNA damage responses. Science. 316 : 1202-1205